Hand Seamer Tool: Essential Guide to Precision Metal Forming
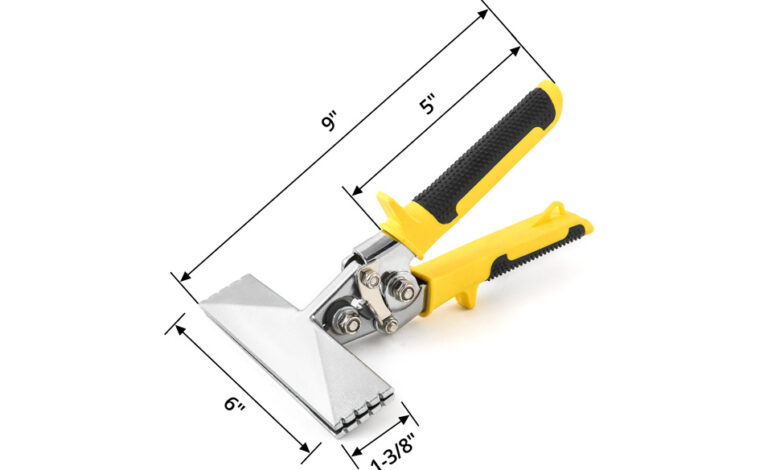
The hand seamer tool is a valuable device used primarily in metalworking and construction. This tool allows users to create precise seams and folds in metal sheets, enhancing the durability and appearance of their projects. Its versatility makes it an essential tool for professionals and DIY enthusiasts alike, providing a reliable method for joining materials seamlessly.
For anyone dealing with metal fabrication, understanding how to use a hand seamer tool efficiently can significantly impact the quality of the work. With various designs available, selecting the right hand seamer can lead to improved productivity and craftsmanship. Knowing the specific applications and techniques can elevate a user’s skills and outcomes.
As projects demand more precise fittings, having a hand seamer in your toolkit can prove to be indispensable. Whether it’s for creating HVAC ducts or crafting intricate metal designs, this tool simplifies tasks that can otherwise be challenging. Exploring the different types and their uses can unlock new potential in any metalworking endeavor.
Essential Features of Hand Seamers
Hand seamers are versatile tools designed for pressing seams and providing a smooth finish to various materials. Key features contribute to their effectiveness, ensuring that users can achieve the desired results efficiently and safely.
Material and Build
The material and construction of a hand seamer significantly impact its durability and performance. Most hand seamers are made from high-quality materials such as steel or aluminum, ensuring strength and resistance to wear.
Heavy-duty models often feature a painted or coated finish, which protects against corrosion. This is especially important for tools used in various environmental conditions. The weight of the tool can also affect usability; a heavier seamer may provide better stability, while a lighter model can offer ease of handling.
Jaw Design and Capacity
The jaw design of a hand seamer plays a crucial role in its functionality. A well-designed jaw allows for efficient heat transfer, essential for fabric fusing applications. Different models may have varying jaw widths, typically ranging from 1 inch to 3 inches.
Users should select a jaw capacity that suits their specific tasks, as larger jaws can accommodate wider materials. Additionally, the edges of the jaw may be smooth or serrated, impacting the grip on the fabric. Smooth jaws are ideal for delicate materials, while serrated jaws provide a better hold for thicker materials.
Handles and Grips
Handles are a critical aspect of hand seamers, influencing user comfort and control during operation. Ergonomically designed handles reduce hand fatigue and strain, making long periods of use more manageable.
Materials such as rubber or molded plastic are commonly used for grips, offering better traction and comfort. Adjustable handles can also enhance usability, allowing users to customize the tool for their grip style. The design should prioritize ease of pressure application to ensure consistent results with minimal effort.
Proper Usage and Maintenance
Proper operation and care of a hand seamer tool enhance its efficiency and longevity. Adhering to specific techniques, alongside regular cleaning and maintenance, will ensure optimal performance.
Operating Techniques
When using a hand seamer, hold it firmly with both hands to provide stability during operation. It is crucial to align the edges of the materials precisely before sealing. Gradually apply pressure while moving the tool along the seam.
Using consistent speed is essential; moving too quickly can lead to incomplete seals. For thicker materials, consider preheating the area for better results.
It is also vital to ensure that the heating element is functioning correctly. Regular checks on the temperature settings help avoid overheating, which can damage materials.
Cleaning and Storage
After each use, the hand seamer should be cleaned to remove residues. Use a soft cloth or brush to wipe down the surfaces. Avoid harsh chemicals that could damage the tool.
For storage, keep the hand seamer in its designated case or a dry, cool area. Ensure that the heating element is completely cooled before storing.
Regularly inspect the tool for signs of wear. If the sealing surfaces become rough or contaminated, replace or clean them as needed. Proper storage prevents physical damage and prolongs the lifespan of the tool.
Common Issues and Fixes
Users may encounter several common issues with hand seamers. A frequent problem is insufficient sealing. This can occur if the tool is not heated enough or if it is moved too quickly. Adjusting the temperature and slowing down the operation usually resolves this issue.
Another issue is an uneven seam. This can result from improper alignment before starting. Ensuring the materials are level and aligned can prevent uneven results.
Lastly, if the hand seamer won’t heat up, check the power source and connections. Faulty plugs or damaged cords may require professional repair or replacement. Regular troubleshooting can minimize downtime and maintain productivity.



